Straightening Process and Principles
The core principles of straightening are “reverse bending” and “elastic-plastic deformation.”
1. Feeding and Loading: One end of the hexagonal steel is fed into the inlet guide cylinder or the first pair of rollers of the straightening machine.
2. Repeated Bending and Plastic Deformation:
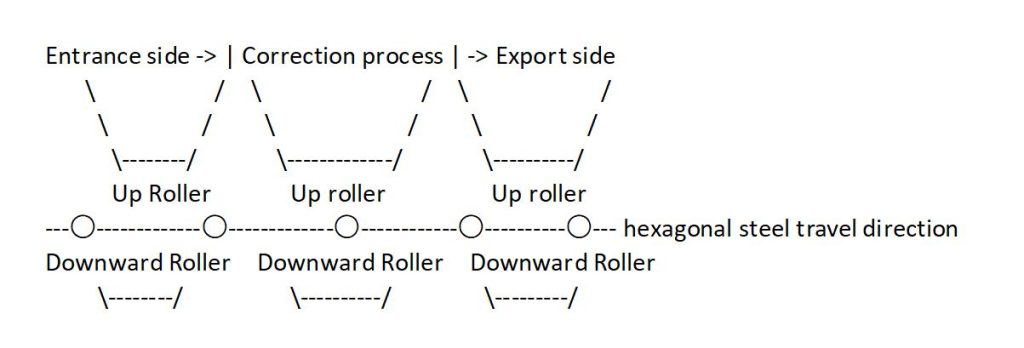
- When the hexagonal steel enters the rollers, it is forced to bend repeatedly in the opposite direction. As shown in the diagram, the middle roller pushes the steel upward, creating a “reverse bend” much larger than the original bend.
- During this reverse bending process, the outer fibers of the steel undergo plastic deformation (permanent deformation) first, while the inner fibers undergo elastic deformation (temporary deformation).
- As the steel continues to move forward and moves away from this maximum bending point, the elastically deformed portion attempts to recover. However, because the outer layer has already undergone plastic deformation, the overall rebound cancels out part of the original bend.
3. Gradual straightening: After multiple small-scale “reverse bending” cycles by a row of staggered rollers (usually 7-11 or more), the internal stress of the hexagonal steel is redistributed, and the residual bending amount gradually decreases.
4. Discharge: Finally, the straightened hexagonal steel is smoothly discharged from the outlet.
Schematic diagram of roller arrangement (side view)
Preparations before processing
1. Inspect Raw Materials: First, visually inspect the hexagonal steel to understand its approximate bending direction and degree.
2. Select and Adjust Equipment:
- Straightening Machine Selection:Roller straightening machines are typically used instead of pressure straightening machines. Roller straightening machines involve continuous rotation and bending, resulting in high efficiency and suitability for batch straightening of long profiles.
- Roller Selection and Arrangement:The upper and lower rows of rollers on the straightening machine are not flat but have hexagonal grooves that match the shape of the hexagonal steel. This ensures that pressure is applied evenly to all six surfaces, preventing damage to edges or rotation.
- Adjust Roller Gap:Adjust the gap between the upper and lower rollers according to the opposite side dimensions of the hexagonal steel (e.g., S22, S30, etc.) to ensure the hexagonal steel can pass smoothly and receive appropriate pressure.
- Adjust the Pressure Reduction:This is the most crucial step. Depending on the degree of curvature, the offset of the middle rollers needs to be adjusted so that they have a “bulge” or “sink” relative to the inlet and outlet rollers. This offset determines the degree of curvature applied during straightening.
Recently, Shanghai ANTISHI Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. received a request from a Russian customer to straighten hexagonal steel. The main workpiece information is as follows:
| Type | Hexagonal steel | round bar | round tube |
| Diameter Range | The circumscribed circle diameter of the hexagon is 41.6 mm. | 20-50mm | 20-50mm |
| Maximum Length | 2400-6000mm | 1000-6000mm | 1000-6000mm |
| Thickness Range | 25mm | / | 5mm |
| Material & Hardness | Hollow hexagonal HEX25, HEX32, HEX35; hexagonal S35
(hardness 38-46 HRC, surface hardness 55-59 HRC).
|
Steel – 23ХН3Мо Steel
Original steel or heat-treated structural steel (core hardness 38-46 HRC, surface hardness 54-58 HRC), workpiece hardness can reach up to 60 HRC. |
Steel – 23ХН3Мо Steel
Original steel or heat-treated structural steel (core hardness 38-46 HRC, surface hardness 54-58 HRC), workpiece hardness can reach up to 60 HRC. |
| Pictures for Reference |  |
 |
 |
Based on the customer’s workpiece information and after multiple discussions, we have matched the following straightening machine model with the following parameters.
| Technical Specifications | Model | ATS-A63-M1 |
| Maximum Loading Force (Nominal Force) | ≤630KN |
| Tabletop Size | 7000*700mm |
| Suitable Workpiece Length | 1000mm≤L≤6000mm |
| Suitable Workpiece Diameter | 20mm≤D≤50mm |
| Number of Straightening Measurement Channels | 1~10(Adjustable within the channel) |
| Sensor Resolution | 0.001mm |
| Repeat Measurement Accuracy | 0.005mm |
| Main Cylinder Idle Speed | 40mm/s |
| Loading Speed | 6~12mm/s |
| Return Speed | 40mm/s |
| R-Axis Rotation Speed | ≤300r/min(Position Servo Driver) |
| X-Axis Running Speed | ≤200mm/s |
| Opening Height | About: 700mm |
| Hydraulic Cylinder Stroke | ≥400mm |
| Equipment Color | ANTISHI color or user-specified |
| Loading Method | Standard pump pneumatic hydraulic loading |
| Spinning Center Type | Roller drive (headstock + tailstock) |
| Spinning Center Drive Type | Servo drive |
| Spinning Center Clamping Type | Friction wheel + pneumatic |
| Tooling Position Setting Type | Manual locking setting |
| Measuring Sensor Type | Measuring rod contact measurement |
| Support Type | Cylinder push rod support |
| Support Block Type | U-shaped support block (long service life, does not damage workpiece) |
| Preset Pressure | Adjustable |
| Straightening Method | Intelligent decision-making automatic straightening (not available for TA2) |
| CNC Stroke Limiting | Program control with two operation modes (touchscreen, button, digital display) |
If you also need a suitable straightening machine for straightening processes, please feel free to contact Shanghai ANTISHI. We are a seasoned supplier of metal machining equipment with extensive experience in machinery manufacturing and application, and can provide you with professional technical support.
Keywords: CNC straightening machine, straightening machine, hexagonal steel straightening machine, round tube straightening machine



