The conventional lathe is one of the most commonly used machines in metalworking. Its basic working principle involves rotating the workpiece while the cutting tool moves along a predetermined path, using cutting force to remove excess material and shape the piece to the desired dimensions. Due to its simple structure, high machining accuracy, and wide range of applications, the conventional lathe is extensively used. We will begin with an overview of the lathe’s structure and explain the functions and working principles of each key component.
1.1 A conventional lathe mainly consists of the following major parts:
Bed: The base structure of the machine, providing rigid support and precise guideways for positioning.
Headstock: Located at one end of the bed, it houses the spindle, transmission system, gear mechanism, and lubrication system, and is responsible for rotating the workpiece.
Tailstock: Positioned at the opposite end of the bed, it supports the other end of the workpiece to prevent vibration and deflection. It can also hold different attachments such as drill bits or tapping tools.
Carriage and Tool Post (Turning Section): Mounted on the saddle, it holds the cutting tools and controls feed motion, allowing manual or automatic feed during the cutting process.
Feed Mechanism: Comprising lead screw, feed rod, shifting mechanism, and control devices, it enables longitudinal, transverse (or diagonal) feed movement of the cutting tool.
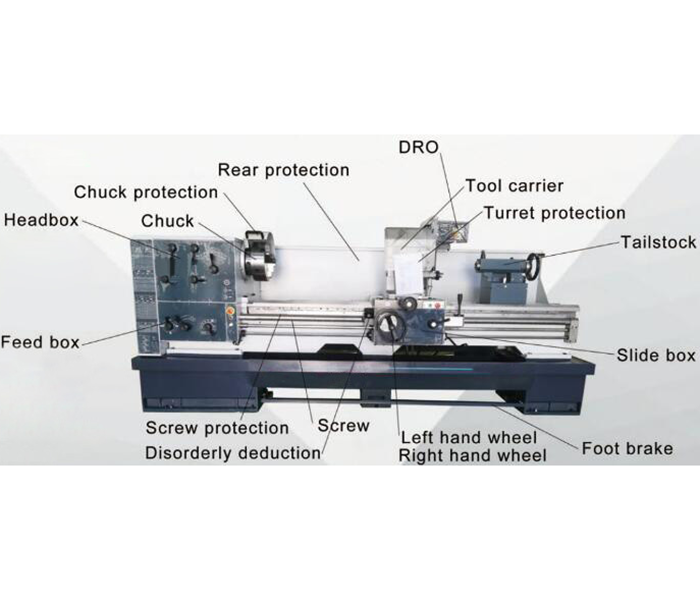
2.1 Bed
Function – The lathe bed serves as the foundational support component of the machine. It provides positioning, load-bearing capacity, and transmits cutting forces. Its surface is typically machined with precision guideways to ensure that all parts of the lathe move in accurately aligned and parallel directions, while minimizing vibrations and deviations introduced during machining.
Working Principle – The bed maintains the rigidity of the entire machine through its stable structure and withstands the impact forces generated by spindle rotation and cutting operations. The guideways are usually heat-treated or induction-hardened to enhance wear resistance and ensure high positioning accuracy.
2.2 Headstock
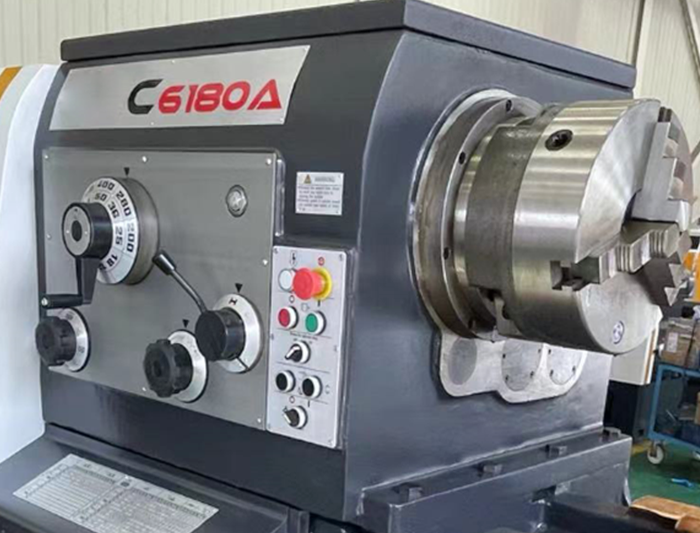

Function – The headstock is the “heart” of the lathe. It houses the spindle, speed-change mechanism, and transmission system. Its main task is to drive the spindle via the motor, enabling rotation of the workpiece. It also allows for speed adjustments, forward and reverse rotation, and meets the speed variation requirements during cutting operations.
Working Principle
Transmission Mechanism: Composed of a gearbox and gear sets, it transmits torque from the motor to the spindle and adjusts spindle speed according to the machining requirements of the workpiece.
Lubrication and Sealing: An internal lubrication system ensures smooth operation of all transmission components, while sealing measures prevent oil leakage and maintain a clean internal environment.
Attachment Mounting: The front end of the spindle is typically fitted with a chuck or other fixtures used to securely hold the workpiece.
2.3 Tailstock
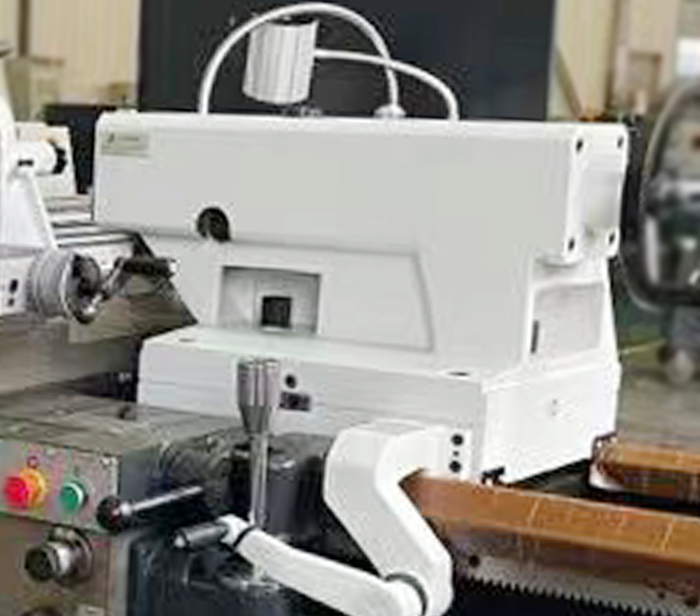

Function – The tailstock is primarily used to support the opposite end of the workpiece, preventing bending or vibration during turning, especially when working with long parts. It can also hold various tools (such as drill bits or taps) to perform internal machining operations like boring, drilling, and tapping.
Working Principle – The tailstock can be moved along the bed guideways to accommodate workpieces of different lengths. Once fixed in place, its internal taper structure allows for secure tool mounting, enabling the transmission of cutting forces and ensuring the workpiece remains stably rotated during machining.
2.4 Carriage and Tool Post
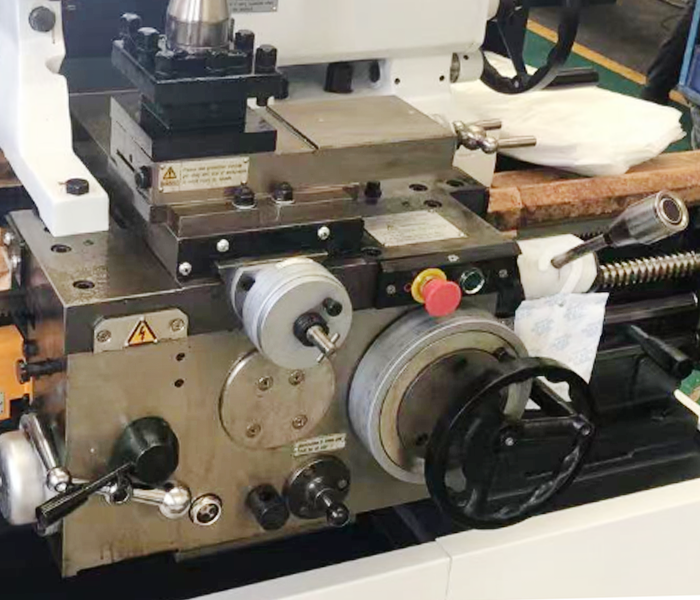
Function – The apron box is mounted on the saddle and contains feed mechanisms and handles that control the longitudinal and transverse movement of the tool post. The tool post holds one or multiple tools (such as in a tool turret) and enables cutting operations through tool movement.
Working Principle
Feed Mechanism: Primarily composed of a lead screw or feed rod along with a gear shifting mechanism. Handles, forks, and connecting rods transmit operating force to move the tool post in the preset direction and feed rate.
Manual and Automatic Control: Most modern conventional lathes support manual operation (via handwheels for adjusting feed rate and direction), and some are equipped with semi-automatic or fully automatic feed functions, which are especially useful for thread cutting or continuous machining.
Interlock Mechanism: To prevent incorrect operation or interference between different control actions, the apron box is also equipped with mechanical and electrical interlocks.
2.5 Feed Mechanism
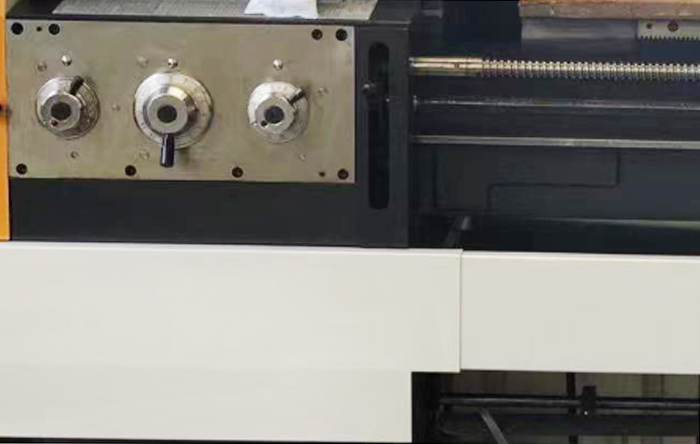

Function – The feed mechanism is responsible for converting the operator’s control inputs into actual feed motion of the tool or workpiece. The main transmission types include lead screw drive and feed rod drive, which work in conjunction with a gearbox to adjust the feed rate and cutting speed.
Working Principle
Lead Screw Drive: Utilizes a threaded lead screw and a matching half-nut to achieve precise linear motion. This method is commonly used for threading operations or low-speed feeds requiring high accuracy.
Feed Rod Drive: Typically used for automatic feed operations. It converts the spindle’s rotational motion into linear motion of the tool post via gears and linkages. It is suitable for larger feed rates and faster cutting tasks.
As a fundamental piece of equipment in metalworking, the conventional lathe may have relatively simple components, but each part plays an irreplaceable role. The bed provides rigid support and precise guidance; the headstock ensures accurate rotation of the workpiece; the tailstock and carriage maintain machining stability; and the feed mechanism transforms operator commands into precise cutting motions. A proper understanding and mastery of how these components work is crucial for improving machining quality and ensuring the stable operation of the lathe.
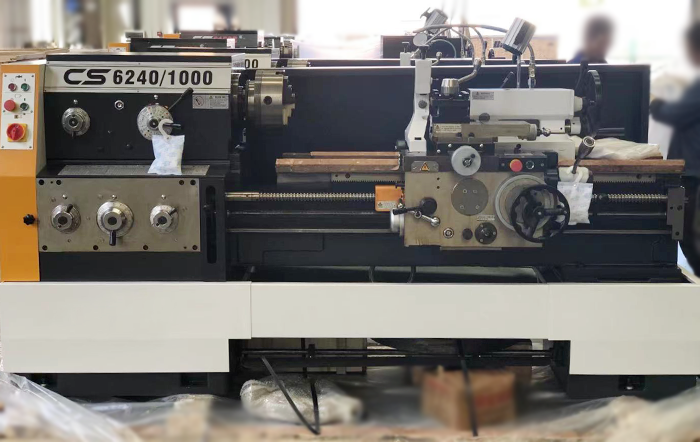
CS Series Horizontal Conventional Lathe
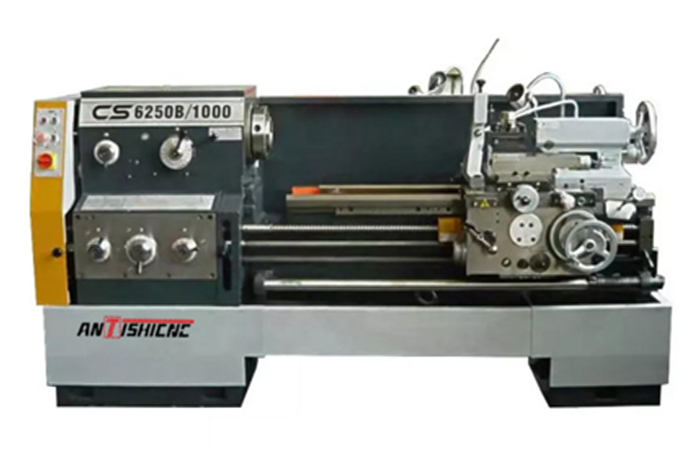

Our CS Series Horizontal Conventional Lathes are fully functional and well-structured, ideal for a wide range of turning operations on rotary parts. They are capable of external and internal turning, taper turning, facing, as well as machining both standard and irregular-shaped parts.The lathes can also cut various metric, imperial, module, and diametral pitch threads. In addition to turning, they support auxiliary operations such as drilling, reaming, and oil groove broaching.Equipped with a large through-hole spindle, they can accommodate workpieces of larger diameters, significantly enhancing machining flexibility.The machines can be configured with either metric or imperial feed systems to meet the measurement standards of different regions.For increased operational safety, both hand brake and foot brake options are available.The electrical system supports multiple voltages (220V, 380V, 420V) and frequencies (50Hz, 60Hz), making the lathes adaptable to different power supply requirements worldwide.Whether for small-batch production or maintenance tasks, this series is an ideal choice.
The CS Series Conventional Lathes are widely used in industries such as machinery manufacturing, metalworking, maintenance services, and mold making. They are particularly effective for small to medium-sized part production and individual part machining, excelling in the following areas:
Processing and repair of engine parts, shafts, flanges, and other components;
Manufacturing and repair of parts for the automotive, motorcycle, and power machinery industries.Precision machining of metal structures, equipment components, and basic mold parts.
If you have similar needs, feel free to contact Shanghai Ants Machine at contact@antsmachine.com.Our technical team will be pleased to provide you with the most suitable technical solution.


